Japan's wind power goals lag far behind the world's capacity ambitions
Dreams of higher wind capacity are blown away.
Post-Fukushima Japan has been in need of other forms of renewable energy. It has been trying to harness the power of wind, but political and geographical circumstances are blowing its chances away of being one of the leaders in the wind sector.
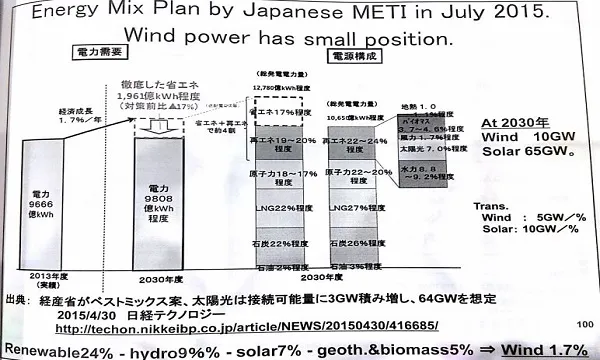
Japan's wind power share in its electricity mix is much lower compared to the rest of the world. It only has 0.5% share in new installations and the capacity hits a measly 3.1GW which earns it the 19th spot in the global list of newly installed power plants.
Currently, Japan is aiming to boost its wind power share to 1.7% or 10GW by 2020 and 36GW by 2030 in its energy mix plan. This, in comparison to China's plans of achieving 250GW by 2020 and India's goal of hitting 60GW by 2022, puts the country behind the world's and Asia's wind power capacity ambitions.
"Japan is not so eager in developing its wind power in the past years," Yoshinori Ueda, general manager, Japan Wind Power Association said in a talk at the World Smart Energy Week 2016. "This is because of the many hurdles against wind power development such as grid restriction."
Japan has shifted to a pro-wind stance since the Fukushima accident, according to Ueda. "But we need more years in order to realize this. We are trying to remove hurdles as of now."
The World Smart Energy Week is happening from today until March 4, 2016 at Tokyo, Japan. The event gathers renowned experts of the smart and renewable energy business fields from across Japan and the world who will share the latest technology and industry trends.








![Cross Domain [Manu + SBR + ABF + ABR + FMCG + HBR + ]](https://cmg-qa.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/styles/exclusive_featured_article/public/2025-01/earth-3537401_1920_4.jpg.webp?itok=WaRpTJwE)
![Cross Domain [SBR + ABR]](https://cmg-qa.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/styles/exclusive_featured_article/public/2025-01/pexels-jahoo-867092-2_1.jpg.webp?itok=o7MUL1oO)









 Advertise
Advertise


